The convergence of advanced technology and the healthcare industry is reshaping the patient experience, streamlining medical procedures, and pushing the boundaries of what's possible in diagnostics and treatments. One such technology that's been capturing the imagination of medical professionals around the globe is augmented reality (AR).
In this extensive exploration, we'll discover how AR is revolutionizing healthcare, enhancing patient outcomes, and paving the way for a new era of medical practice.
Augmented reality (AR) is not just a tool for entertainment or gaming but a formidable ally in the healthcare provider's arsenal. By blending the digital world with the real, AR applications enable healthcare professionals to perform surgeries with greater precision, facilitate patient education, and improve therapy adherence, opening a new chapter in the book of medical innovation.
The Anatomical Overlay: AR's Role in Surgical Precision
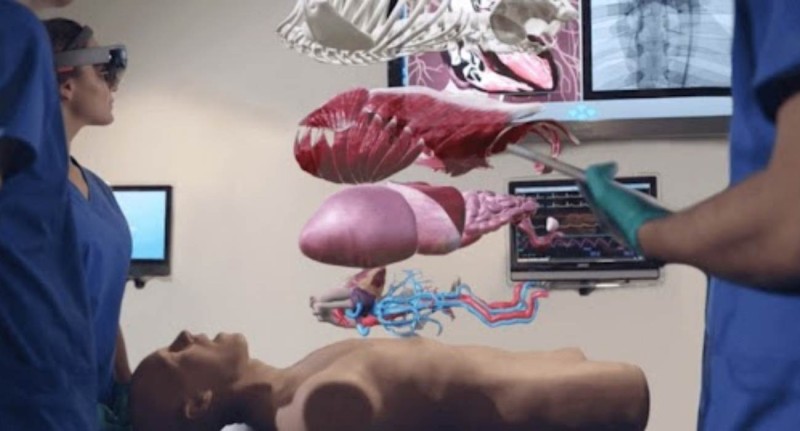
In complex surgeries, where the margin of error is as thin as a scalpel blade, AR has proved to be a game-changer. With systems that overlay critical information, such as a patient's anatomy, including veins and arteries, onto the surgeon's field of vision, once high-risk surgeries are now navigated with enhanced precision and safety.
Case in Point: Merging MRI with Real-Time Vision
Surgeons no longer have to rely solely on their physical sight and pre-operative scans. AR systems merge MRI or CT scan images with the patient's real-time anatomy, allowing for on-the-fly adjustments and ensuring no crucial structures are inadvertently damaged.
The Benefits Beyond Visuals
Aside from the obvious benefit of providing a 'roadmap' for the surgeon, AR systems allow for less invasive procedures, shorter recovery times, and the capability to perform otherwise complex operations, even for less experienced surgeons under the mentorship of their digital augmentation.
AR and Patient Education: Seeing is Believing
Learning about complex medical conditions can be a daunting task for patients. AR bridges this knowledge gap by providing a visual understanding that printed materials or verbal descriptions alone cannot convey.
Interactive Learning Experiences
Imagine a patient able to see a three-dimensional model of their heart defect, explore it from various angles, and understand the planned corrective surgery. This level of interactivity not only educates but also empowers the patient, potentially reducing pre- and postoperative anxiety and improving overall engagement in their treatment plan.
Customized Patient Information
AR applications also allow for the creation of personalized information for the patient, tailored to their specific medical condition and treatment plan. This tailoring ensures the patient receives the most relevant and digestible information, which aids in effective communication between the healthcare provider and the patient.
Bridging Gaps in Therapy Adherence with AR
Nonadherence to prescribed therapies is a common challenge in healthcare, leading to poorer treatment outcomes and increased healthcare costs. AR interventions have shown promise in improving adherence rates by making therapy regimes more accessible and user-friendly.
Visual and Auditory Reminders
AR can be utilized to provide patients with both visual and auditory reminders for their medication schedules or rehabilitation exercises, making it harder to forget or ignore their treatment plan. The interactive nature of AR also makes these reminders more engaging, turning a task into a game-like experience.
Personalized Virtual Monitoring
Using AR for remote monitoring and personalized virtual care can improve patient-clinician interaction, allowing healthcare providers to keep a closer eye on their patient's progress and intervene with support or adjustments as needed. This level of personalized follow-up can boost patient confidence and the sense of being cared for, which can significantly impact therapeutic adherence.
Looking Ahead: The Future of AR in Health
As with any emerging technology, the potential for Augmented Reality in healthcare is vast, and ongoing research and development are uncovering new possibilities regularly.
AR in Medical Training and Education
The application of AR in medical education allows for immersive, hands-on learning experiences like never before. Medical students can interact with virtual patients, simulate surgeries, and visualize complex biological processes in real-time, all contributing to a more thorough and practical educational experience.
AR in Health Monitoring and Early Diagnostics
Wearable AR devices could potentially monitor a patient's health indicators in real-time, providing early warnings for potential health issues and promoting proactive care. Such devices could also offer a more comfortable and less obtrusive means for continuous health monitoring, especially for elderly or chronically ill patients.
Ethical Considerations and the Path Forward
The integration of AR in healthcare is not without its challenges. Ethical concerns regarding patient privacy, data security, and the digital divide need to be addressed. Regulatory bodies will also need to evolve to provide guidelines and oversight for the use of AR in clinical settings.
The Takeaway
Augmented reality is not a distant promise but a reality for the healthcare sector. From revolutionizing surgery to improving patient understanding and adherence, AR is proving to be a powerful force in the quest for better health outcomes.
As we navigate this new terrain, the focus remains on leveraging technology to humanize and personalize patient care. AR promises that it can make complex and overwhelming processes visible, understandable, and, ultimately, more manageable for patients and providers alike.
It's an exciting time to be at the crossroads of healthcare and technology. If you look to explore the depths of AR's potential in healthcare, consider signing up for no-code platforms like PlugXR. It is a go-to platform for all things AR without needing coding expertise!